What is a stepper motor?
Before we dive into the realm of music creation, let's first understand what stepper motors are. Stepper motors are a type of electric motor that converts electrical pulses into precise mechanical movements. Unlike regular DC motors, stepper motors move in discrete steps, allowing for precise control and positioning. These motors are widely used in various industries, including robotics, automation, and now, music production.
Stepper motors are designed with a unique construction that enables them to rotate in small, fixed increments called steps. These steps can be as small as 1.8 degrees per step, providing incredible accuracy and control. The movement of a stepper motor is achieved by energizing coils in a specific sequence, causing the rotor to move in a precise manner.
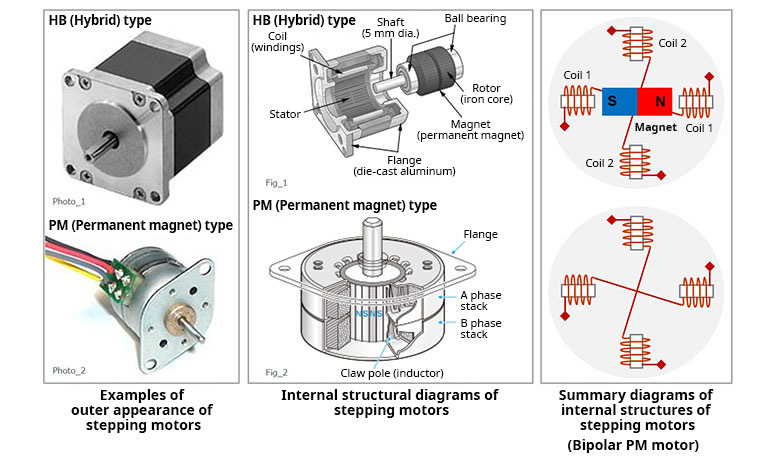
How can they be used in music?
In the realm of music production, stepper motors have found a fascinating application. They are being used to create innovative and interactive musical instruments. These instruments, often referred to as "motor-controlled musical devices," utilize the precise movement of stepper motors to generate unique sounds and rhythms.
One example of a motor-controlled musical device is the Motor Synth. Developed by a team of engineers and musicians, this instrument combines traditional synthesis techniques with the mechanical movement of stepper motors. The Motor Synth features multiple stepper motors, each controlling a different parameter of the sound, such as pitch, modulation, or filter cutoff. By manipulating the speed and direction of the stepper motors, musicians can create complex and evolving musical patterns.
Another exciting application of stepper motors in music production is the creation of robotic drummers. These robotic drummers use stepper motors to strike percussion instruments with incredible precision and timing. By programming the movement of the stepper motors, musicians can achieve complex drumming patterns that would be challenging for a human drummer to replicate consistently. Stepper motors have also been integrated into MIDI controllers, allowing musicians to control various parameters of their music production software using physical knobs and sliders. These controllers use stepper motors to provide tactile feedback, giving the user a more intuitive and immersive experience.
From motor-controlled synthesizers to robotic drummers, stepper motors have opened up new possibilities in music production, allowing musicians to explore uncharted territories of sound and rhythm.
What is MIDI?
MIDI has revolutionized the way music is created, produced, and performed. Before the advent of MIDI, musicians relied on analog instruments and physical connections to create and record music. This limited their ability to experiment with different sounds and effects, and made the process of composing and arranging music a time-consuming and labor-intensive task.
With MIDI, musicians can now connect their instruments, such as keyboards, guitars, and drum machines, to a computer or other MIDI-enabled devices. This allows them to control and manipulate the sounds produced by their instruments in real time, opening up a world of creative possibilities.
One of the key advantages of MIDI is its ability to separate the sound generation from the control of the music. In other words, MIDI messages do not transmit actual audio signals, but rather instructions on how to produce those sounds. This means that musicians can use MIDI to control multiple instruments simultaneously, triggering different sounds and effects with a single keystroke or command.
Another important feature of MIDI is its flexibility and versatility. MIDI data can be easily edited, manipulated, and rearranged using software programs known as sequencers. These programs allow musicians to change the tempo, key, and timing of their compositions, as well as add additional layers of instrumentation and effects.
MIDI allows for seamless integration between different devices and software platforms. Musicians can use MIDI to connect their instruments to a computer, and then use software programs to record, edit, and mix their music. MIDI also makes it possible to synchronize multiple devices, such as synthesizers, drum machines, and sequencers, so that they all play in perfect time with each other.
Whether it's composing a symphony, producing a pop song, or performing live on stage, MIDI has become an essential tool for musicians of all genres and styles.
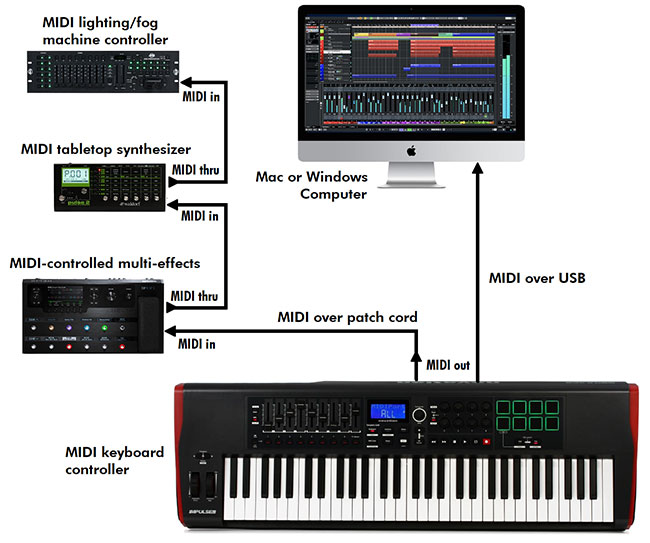
Combining Stepper Motors and MIDI
Now that we have a basic understanding of stepper motors and MIDI, let's explore how these two technologies can be combined to create music. By connecting stepper motors to MIDI-controlled devices, musicians can turn the mechanical movements of the motors into musical notes and rhythms.
One way to achieve this is by attaching various objects, such as drumsticks or mallets, to the stepper motors. As the motors rotate, the attached objects can strike different surfaces, producing unique sounds. By controlling the speed and direction of the motors, musicians can create rhythmic patterns and beats.
Another approach is to use stepper motors to control the position of musical instruments, such as guitars or keyboards. By attaching stepper motors to the instrument's strings or keys, musicians can automate the playing process. This opens up a whole new world of possibilities, allowing for complex melodies and harmonies that would be challenging to achieve manually.
Additionally, stepper motors can be used to create dynamic visual effects during live performances. By attaching LEDs or other lighting elements to the motors, musicians can synchronize the movement of the lights with the music, enhancing the overall visual experience for the audience.
Stepper motors can be integrated into MIDI-controlled robotic systems, adding a layer of interactivity to the performance. For example, a robotic arm controlled by stepper motors could play a drum set or a xylophone, responding to MIDI signals in real-time. This fusion of technology and music not only creates a captivating performance but also pushes the boundaries of what is possible in terms of musical expression.
Credits
Special thanks to Alexis Garado & David Scholten for the inspiration behind this article.
